FOCUS / CLARITY / MEMORY
Advanced Focus & Energy
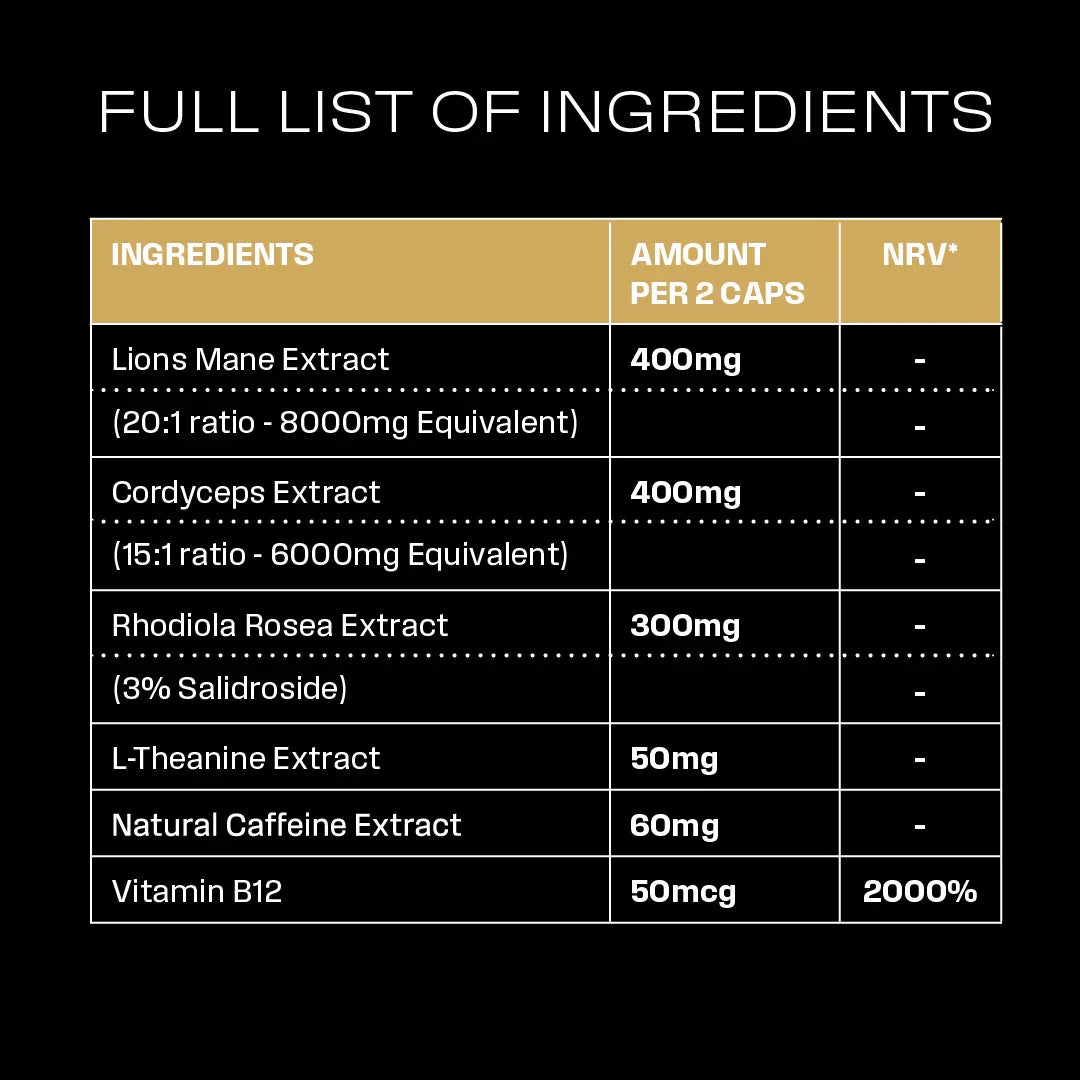
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Improving effects of the mushroom Hericium erinaceus on mild cognitive impairment: a double‑blind placebo‑controlled clinical trial – Mori et al. (2009)
Findings: Hericium erinaceus (Yamabushitake) significantly improved cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment over 16 weeks, with no adverse effects..
Read the full study here
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
The Acute and Chronic Effects of Lion's Mane Mushroom Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Stress and Mood in Young Adults: A Double-Blind Study - Doucherty et al (2023)
Findings: A single 1.8g dose of Hericium erinaceus significantly improved cognitive speed in healthy young adults, with signs of reduced stress after 28 days.
Read the full study
Cordyceps | STUDY 1
Cordyceps | STUDY 1
Improvement of Learning and Memory Induced by Cordyceps Polypeptide Treatment and the Underlying Mechanism - Yuan Et al 2018
Findings: Cordyceps polypeptides improved learning and memory by reducing oxidative stress and modulating key neuroprotective genes
Read the full study
Cordyceps | STUDY 2
Cordyceps | STUDY 2
Effect of Cs-4 (Cordyceps) on exercise performance in healthy older subjects: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - Chen et al 2009
Findings: Cordyceps (Cs-4) improved exercise performance in healthy older adults, raising metabolic threshold by 10.5% over 12 weeks.
Read the full study
Rhodiola | STUDY 1
Rhodiola | STUDY 1
Rhodiola rosea in stress-induced fatigue – a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study – Darbinyan et al. (2000)
Findings: Rhodiola rosea significantly reduced mental fatigue and improved cognitive performance in physicians working night shifts, with no reported side effects.
Read the full study
Rhodiola | STUDY 2
Rhodiola | STUDY 2
A randomized trial of Rhodiola rosea SHR‑5 extract in the treatment of stress‑related fatigue – Shevtsov et al. (2003)
Findings: A single dose of Rhodiola rosea significantly boosted mental performance under fatigue, with both tested doses outperforming placebo (p < 0.001).
L-Theanine | STUDY 1
L-Theanine | STUDY 1
L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state - Nobre et al 2008
Findings: A 50mg dose of L-theanine significantly increased alpha brain wave activity, promoting relaxed alertness without drowsiness (p < 0.05).
L-Theanine| STUDY 2
L-Theanine| STUDY 2
The combination of L‑theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance and increases subjective alertness – Giesbrecht et al. (2010)
Findings: A 97mg L-theanine + 40mg caffeine blend significantly improved task-switching accuracy and alertness while reducing tiredness in young adults
Read the full study
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows the rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial – Smith et al. (2010)
Findings: Low vitamin B-12 status and elevated homocysteine or MMA levels significantly accelerated cognitive decline, while folate showed no effect.
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 and cognitive function in older persons – Doets et al. 2012
Findings: low levels of sensitive markers like MMA and holotranscobalamin were associated with cognitive decline.
Read the full study
Caffeine | STUDY 1
Caffeine | STUDY 1
Cognitive and mood improvements following caffeine administration in healthy volunteers – Haskell et al. (2005)
Findings: Caffeine improved attention, memory speed, and alertness in both users and non-users, independent of withdrawal, with different benefits by group.
Caffeine | STUDY 2
Caffeine | STUDY 2
Caffeine as an attention enhancer: a review – Einöther & Giesbrecht (2013)
Findings: Caffeine reliably enhances attention across both simple and complex tasks, including alerting and executive control, beyond just reversing withdrawal.
Read the full study
PERFORMANCE / LONGEVITY / ENERGY
Advanced NMN Complex

NMN | STUDY 1
NMN | STUDY 1
Nicotinamide Riboside Augments the Aged Human Skeletal Muscle NAD+ Metabolome and Induces Transcriptomic and Anti-inflammatory Signatures – Elhassan et al. (2019)
Findings: Daily supplementation with 1 g of nicotinamide riboside for 21 days increased skeletal muscle NAD⁺ metabolites and reduced inflammatory markers in aged men.
Read the full study here
NMN | STUDY 2
NMN | STUDY 2
The Safety and Antiaging Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Human Clinical Trials: an Update – Song et al. (2023)
Findings: Human trials suggest that nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) safely increases NAD⁺ levels and may offer protective effects against age-related decline.
Read the full study
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 1
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 1
Betaine supplementation decreases plasma homocysteine in healthy adult participants: a meta-analysis – McRae (2013)
Findings: Daily supplementation with 4 g or more of betaine for at least 6 weeks significantly reduces plasma homocysteine in healthy adults..
Read the full study here
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 2
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 2
Effects of betaine supplementation on cardiovascular markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis – Ashtary-Larky et al. (2021)
Findings: Betaine supplementation significantly lowers homocysteine levels but may raise LDL and total cholesterol at doses ≥4 g/day.
Read the full study
Quercetin | STUDY 1
Quercetin | STUDY 1
Mechanisms of Neuroprotection by Quercetin: Counteracting Oxidative Stress and More – Costa et al. (2016)
Findings: Quercetin shows neuroprotective effects through antioxidant activity, sirtuin activation, and cellular defense pathway modulation
Read the full study here
Quercetin | STUDY 2
Quercetin | STUDY 2
Recent Advances in Potential Health Benefits of Quercetin – Aghababaei & Hadidi (2023)
Findings: Quercetin demonstrates strong antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties, with emerging potential across multiple health domains.
Read the full study
Pterostilbene | STUDY 1
Pterostilbene | STUDY 1
Unlocking the therapeutic potential of natural stilbene: Exploring pterostilbene as a powerful ally against aging and cognitive decline – Dutta et al. (2023)
Findings: Pterostilbene shows strong potential to combat aging and cognitive decline by targeting oxidative stress, inflammation, and neural function.
Pterostilbene | STUDY 2
Pterostilbene | STUDY 2
Pterostilbene in the treatment of inflammatory and oncological diseases – Liu et al. (2024)
Findings: Pterostilbene shows strong anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential with superior bioavailability.
Read the full study here
Trans-Resveratrol | STUDY 1
Trans-Resveratrol | STUDY 1
Effects of resveratrol on memory performance, hippocampal functional connectivity, and glucose metabolism in healthy older adults – Witte et al. (2014)
Findings: 200 mg of resveratrol daily for 26 weeks improved memory retention and hippocampal connectivity in healthy adults.
Read the full study here
Trans-Resveratrol | STUDY 2
Trans-Resveratrol | STUDY 2
Effects of resveratrol on cerebral blood flow variables and cognitive performance in humans: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover investigation – Kennedy et al. (2010)
Findings: Single doses of 250 mg and 500 mg trans-resveratrol significantly increased cerebral blood flow during cognitive task performance in healthy adults.
Read the full study
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows the rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial – Smith et al. (2010)
Findings: Low vitamin B-12 status and elevated homocysteine or MMA levels significantly accelerated cognitive decline, while folate showed no effect.
Read the full study here
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 and cognitive function in older persons – Doets et al. 2012
Findings: Low levels of sensitive markers like MMA and holotranscobalamin were associated with cognitive decline.
Read the full study
STRENGTH / RESILIENCE / ENDURANCE
Advanced Shilajit Complex
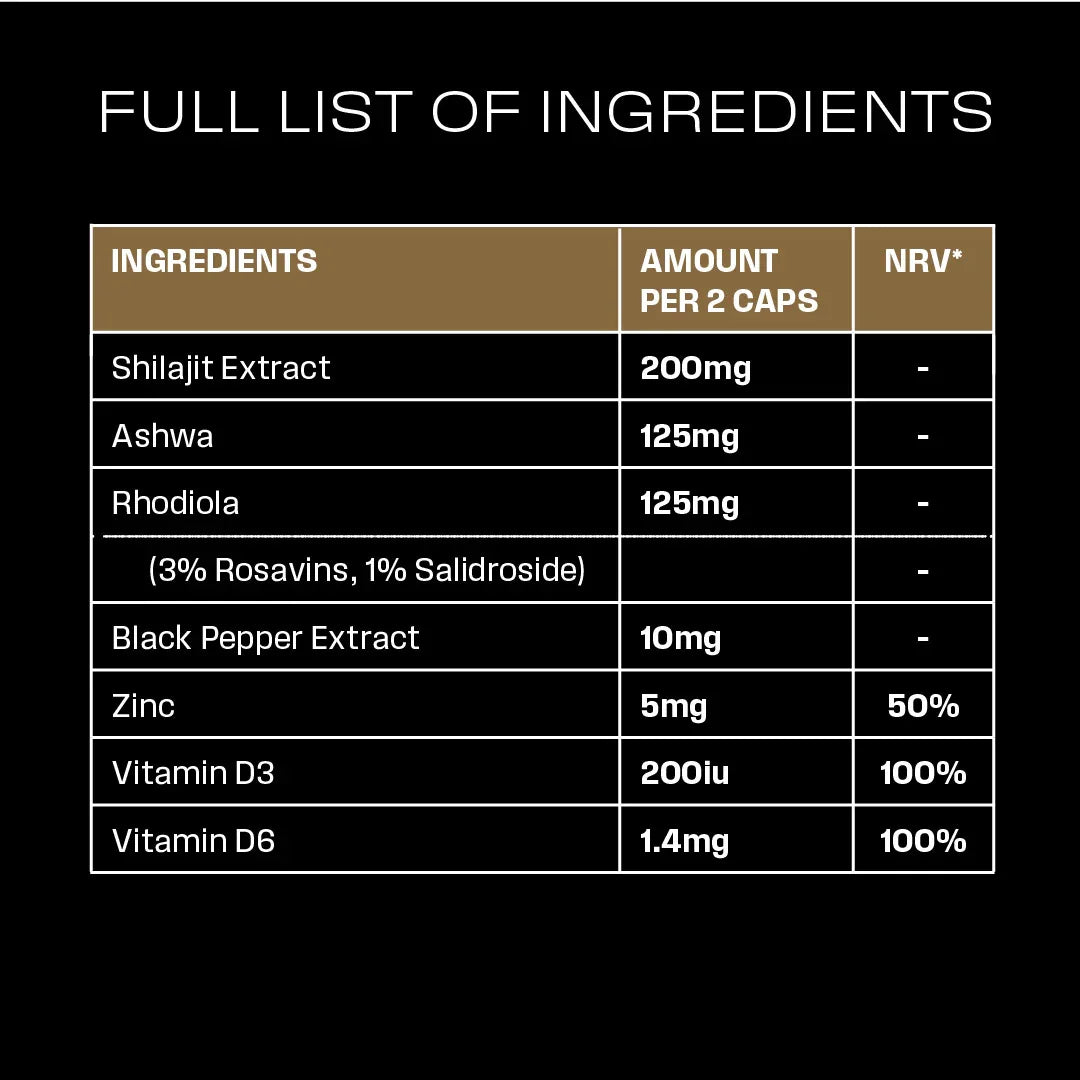
Shilajit | STUDY 1
Shilajit | STUDY 1
Clinical evaluation of purified Shilajit on testosterone levels in healthy volunteers - Pandit et al - 2016
Findings: Daily supplementation with purified Shilajit significantly increased total and free testosterone, as well as DHEAS, in healthy middle-aged men.
Read the full study here
Shilajit | STUDY 2
Shilajit | STUDY 2
The effects of Shilajit supplementation on fatigue-induced decreases in muscular strength and serum hydroxyproline levels - Keller et al (2019)
Findings: Eight weeks of 500 mg/day Shilajit significantly improved strength retention and reduced muscle breakdown markers in recreationally active men.
Read the full study
Ashwagandha | STUDY 1
Ashwagandha | STUDY 1
Placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults – Chandrasekhar et al. (2012)
300 mg of high-concentration Ashwagandha root extract taken twice daily for 60 days significantly reduced stress and cortisol levels in chronically stressed adults.
Read the full study here
Ashwagandha | STUDY 2
Ashwagandha | STUDY 2
Effect of standardized aqueous extract of Withania somnifera on tests of cognitive and psychomotor performance in healthy human participants – Pingali et al. (2014)
Findings: 500 mg/day of aqueous Ashwagandha extract for 14 days significantly improved multiple markers of cognitive and psychomotor performance in healthy adults compared to placebo
Read the full study
Rhodiola | STUDY 1
Rhodiola | STUDY 1
Rhodiola rosea in stress-induced fatigue – a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study – Darbinyan et al. (2000)
Findings: Rhodiola rosea significantly reduced mental fatigue and improved cognitive performance in physicians working night shifts, with no reported side effects.
Read the full study here
Rhodiola | STUDY 2
Rhodiola | STUDY 2
A randomized trial of Rhodiola rosea SHR‑5 extract in the treatment of stress‑related fatigue – Shevtsov et al. (2003)
Findings: A single dose of Rhodiola rosea significantly boosted mental performance under fatigue, with both tested doses outperforming placebo (p < 0.001).
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers – Shoba et al. (1998)
Findings: Piperine significantly enhances the absorption and bioavailability of curcumin in both rats and humans, overcoming curcumin’s naturally poor uptake.
Read the full study here
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by combining it with piperine – Johnson et al. (2011)
Findings: Co-administering piperine with resveratrol significantly increased resveratrol’s bioavailability and peak serum concentration in mice.
Read the full study
Zinc | STUDY 1
Zinc | STUDY 1
Zinc and human health: an update – Chasapis et al. (2012)
Findings:
Zinc plays a crucial role in immune function, oxidative stress regulation, and chronic disease prevention, with deficiency linked to a wide range of health issues.
Read the full study
Zinc | STUDY 2
Zinc | STUDY 2
Effects of zinc supplementation on cognitive function in healthy middle-aged and older adults: the ZENITH study – Maylor et al. (2006)
Findings:
Zinc supplementation showed modest short-term cognitive benefits in healthy older adults, particularly in spatial working memory.
Read the full study
Vitamin D | STUDY 1
Vitamin D | STUDY 1
Meta-analysis of memory and executive dysfunctions in relation to vitamin D – Annweiler et al. (2013)
Findings:
Lower vitamin D levels are significantly associated with executive dysfunction, particularly in mental shifting and processing speed, but show only modest links to episodic memory.
Vitamin D | STUDY 2
Vitamin D | STUDY 2
Vitamin D and cognition in older adults: updated international recommendations – Annweiler et al. (2014)
Findings: International experts agree that vitamin D deficiency increases dementia risk in older adults and warrants screening, though it is not yet a diagnostic tool for cognitive decline.
Read the full study
Vitamin B | STUDY 1
Vitamin B | STUDY 1
Effect of Vitamin B Supplementation on Cognitive Function – Ford & Almeida (2019)
Findings: Vitamin B supplementation lowers homocysteine levels in older adults
Read the full study
Vitamin B | STUDY 2
Vitamin B | STUDY 2
B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review – Kennedy (2016)
Findings: B-vitamin supplementation at doses higher than current RDAs may offer a more effective strategy for supporting long-term cognitive and neurological function.
CALM / BALANCE / RESILIENCE
Advanced Ashwagandha KSM-66

Ashwagandha | STUDY 1
Ashwagandha | STUDY 1
Placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy of a high-concentration full-spectrum extract of ashwagandha root in reducing stress and anxiety in adults – Chandrasekhar et al. (2012)
300 mg of high-concentration Ashwagandha root extract taken twice daily for 60 days significantly reduced stress and cortisol levels in chronically stressed adults.
Read the full study here
Ashwagandha | STUDY 2
Ashwagandha | STUDY 2
Effect of standardized aqueous extract of Withania somnifera on tests of cognitive and psychomotor performance in healthy human participants – Pingali et al. (2014)
Findings: 500 mg/day of aqueous Ashwagandha extract for 14 days significantly improved multiple markers of cognitive and psychomotor performance in healthy adults compared to placebo
Read the full study
REST / RECOVERY / RENEWAL
Advanced Sleep Complex

Tyrosine | STUDY 1
Tyrosine | STUDY 1
Tyrosine improves cognitive performance and reduces blood pressure in cadets after one week of a combat training course – Deijen et al. (1999)
Findings: :Tyrosine supplementation improved memory and tracking performance under stress and reduced systolic blood pressure in cadets during combat training.
Read the full study here
Tyrosine | STUDY 2
Tyrosine | STUDY 2
Dietary Tyrosine Protects Striatal Dopamine Receptors from the Adverse Effects of REM Sleep Deprivation – Hamdi et al. (1998)
Findings: Tyrosine supplementation protected dopamine D2 receptor function and reduced behavioral effects caused by REM sleep deprivation in rats.
Read the full study
Lemon Balm | STUDY 1
Lemon Balm | STUDY 1
Modulation of mood and cognitive performance following acute administration of Melissa officinalis (lemon balm) – Kennedy et al. (2002)
Findings: Single doses of lemon balm extract modulated mood and cognitive performance in healthy adults, improving attention but reducing alertness at higher doses.
Read the full study here
Lemon Balm | STUDY 2
Lemon Balm | STUDY 2
Effects of Melissa officinalis Phytosome on Sleep Quality: Results of a Prospective, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, and Cross-Over Study – Di Pierro et al. (2024)
Findings: A bioavailable lemon balm phytosome extract significantly improved sleep quality and slow-wave sleep in adults with mild insomnia.
Read the full study
Chamomile | STUDY 1
Chamomile | STUDY 1
A herbal medicine of the past with bright future – Srivastava et al. (2010)
Findings:
Chamomile has long-standing traditional use and emerging scientific support for its anti-inflammatory, calming, and therapeutic effects across a wide range of conditions.
Read the full study here
Chamomile | STUDY 2
Chamomile | STUDY 2
The effects of chamomile extract on sleep quality: A clinical trial – Adib-Hajbaghery & Mousavi (2017)
Findings: Chamomile extract significantly improved sleep quality in elderly adults after 28 days of supplementation.
Read the full study
Niacin | STUDY 1
Niacin | STUDY 1
The association of sleep quality and insomnia with dietary intake of tryptophan and niacin – Verster et al. (2015)
Findings: Higher dietary intake of tryptophan and niacin was modestly but significantly associated with lower insomnia scores and improved sleep quality, especially in men.
Read the full study here
Niacin | STUDY 2
Niacin | STUDY 2
Nicotinic acid promotes sleep through prostaglandin synthesis in mice – Szentirmai & Kapás (2019)
Findings: Nicotinic acid significantly increased non-REM sleep in mice via prostaglandin-mediated activation of the GPR109A receptor, independent of body temperature changes.
Read the full study
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
A combination of melatonin, vitamin B6 and medicinal plants in the treatment of mild-to-moderate insomnia: A prospective pilot study – Lemoine et al. (2019)
Findings: A 2-week combination of melatonin, vitamin B6, and plant extracts significantly improved sleep quality, onset, and duration in individuals with mild-to-moderate insomnia.
Read the full study here
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 2
B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review – Kennedy (2016)
Findings: All eight B vitamins are essential for brain health.
Read the full study
Magnesium | STUDY 1
Magnesium | STUDY 1
The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial – Abbasi et al. (2012)
Findings: Eight weeks of 500 mg magnesium supplementation significantly improved insomnia symptoms and sleep biomarkers in older adults.
Read the full study here
Magnesium | STUDY 2
Magnesium | STUDY 2
Effectiveness of Magnesium Supplementation on Sleep Quality and Mood for Adults with Poor Sleep Quality: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Crossover Pilot Trial – Breus et al. (2024)
Findings: Two weeks of magnesium significantly improved sleep quality, deep sleep, and mood in adults with poor sleep quality, with no adverse effects.
Read the full study
IMMUNITY / CLARITY / VITALITY
Advanced Mushroom Complex
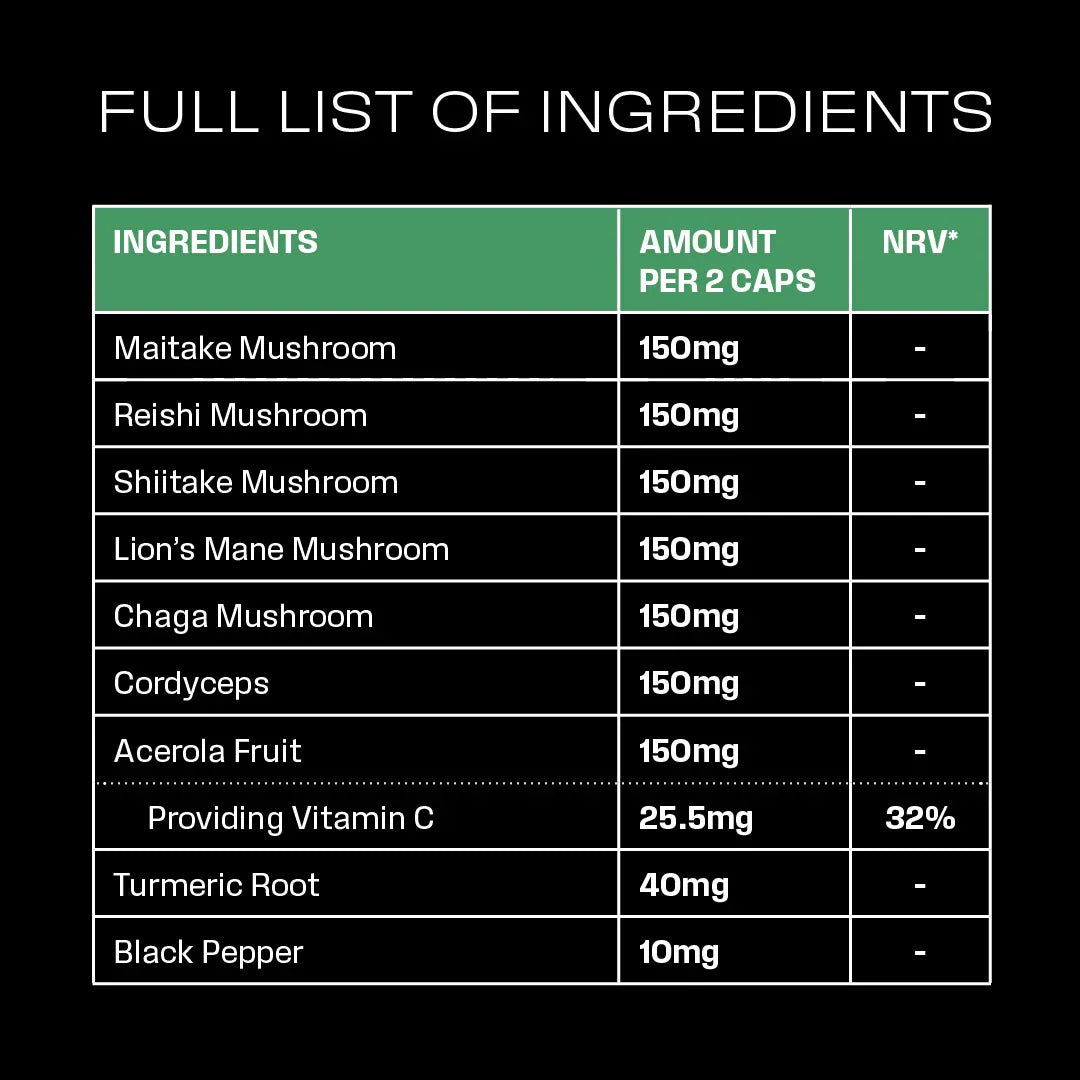
Maitake | STUDY 1
Maitake | STUDY 1
Unveiling the full spectrum of maitake mushrooms: A comprehensive review of their medicinal, therapeutic, nutraceutical, and cosmetic potential – Camilleri et al. (2024)
Findings:
Maitake mushrooms (Grifola frondosa) contain bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential for immune support, metabolic health, and functional food applications.
Read the full study here
Maitake | STUDY 2
Maitake | STUDY 2
Cultivated maitake mushroom demonstrated functional food quality as determined by in vitro bioassays – Dissanayake et al. (2018)
Findings:
Cultivated maitake mushrooms contain unique compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects comparable to standard NSAIDs.
Read the full study
Reishi | STUDY 1
Reishi | STUDY 1
Neuroprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides against oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis – Sun et al. (2017)
Findings:
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides significantly protect neurons from oxidative stress by regulating key apoptotic proteins and reducing cell death.
Read the full study here
Reishi | STUDY 2
Reishi | STUDY 2
Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum Promote Cognitive Function and Neural Progenitor Proliferation in Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease – Huang et al. (2017)
Findings: Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides improved cognitive performance and boosted neural regeneration in an Alzheimer's mouse model via FGFR1 activation.
Read the full study
Shiitake | STUDY 1
Shiitake | STUDY 1
Consuming Lentinula edodes (Shiitake) Mushrooms Daily Improves Human Immunity: A Randomized Dietary Intervention in Healthy Young Adults – Dai et al. (2015)
Findings:
Daily consumption of 5–10 g of dried shiitake mushrooms for 4 weeks significantly improved immune function, enhanced T-cell activation, and reduced inflammation markers in healthy adults.
Read the full study here
Shiitake | STUDY 2
Shiitake | STUDY 2
The Unexplored Anticaries Potential of Shiitake Mushroom – Avinash et al. (2016)
Findings: Shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) contains bioactive compounds with demonstrated anticariogenic, antimicrobial, and oral health-supportive properties.
Read the full study
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Improving effects of the mushroom Hericium erinaceus on mild cognitive impairment: a double‑blind placebo‑controlled clinical trial – Mori et al. (2009)
Findings:
Hericium erinaceus (Yamabushitake) significantly improved cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment over 16 weeks, with no adverse effects.
Read the full study here
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
The Acute and Chronic Effects of Lion's Mane Mushroom Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Stress and Mood in Young Adults - Doucherty et al (2023)
Findings:
A single 1.8g dose of Hericium erinaceus significantly improved cognitive speed in healthy young adults, with signs of reduced stress after 28 days.
Read the full study
Chaga | STUDY 1
Chaga | STUDY 1
Recent Developments in Inonotus obliquus (Chaga mushroom) Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structural Characteristics, Biological Activities and Application – Lu et al. (2021)
Findings: Polysaccharides from Chaga (Inonotus obliquus) show strong antitumor, antioxidant, antiviral, and metabolic benefits, with promising therapeutic potential.
Read the full study here
Chaga | STUDY 2
Chaga | STUDY 2
Chaga mushroom triterpenoids as adjuncts to minimally invasive cancer therapies: A review – Plehn et al. (2023)
Findings: Triterpenoids from Chaga mushrooms, especially inotodiol, show potent cytotoxic effects on cancer cells and may support integrative cancer treatments.
Read the full study
Cordyceps | STUDY 1
Cordyceps | STUDY 1
Improvement of Learning and Memory Induced by Cordyceps Polypeptide Treatment and the Underlying Mechanism - Yuan Et al 2018
Findings:
Cordyceps militaris polypeptides improved learning and memory by reducing oxidative stress and modulating key neuroprotective genes.
Read the full study here
Cordyceps | STUDY 2
Cordyceps | STUDY 2
Effect of Cs-4 (Cordyceps sinensis) on exercise performance in healthy older subjects: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial - Chen et al 2009
Findings:
Cordyceps sinensis (Cs-4) improved exercise performance in healthy older adults, raising metabolic threshold by 10.5% over 12 weeks.
Read the full study
Acerola | STUDY 1
Acerola | STUDY 1
Acerola, an untapped functional superfruit: a review on latest frontiers – Prakash & Baskaran (2018)
Findings:
Acerola is one of the richest natural sources of vitamin C and contains potent phytonutrients with antioxidant, anti-aging, and functional food properties.
Read the full study here
Acerola | STUDY 2
Acerola | STUDY 2
Vitamin C Status and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review – Travica et al. (2017)
Findings:
Higher vitamin C levels are associated with better cognitive performance in healthy individuals, highlighting the nutrient’s neuroprotective potential.
Read the full study
Turmeric Root | STUDY 1
Turmeric Root | STUDY 1
Memory and Brain Amyloid and Tau Effects of a Bioavailable Form of Curcumin in Adults – Small et al. (2017)
Findings:
An 18-month study found that a bioavailable form of curcumin improved memory and attention in adults while reducing brain amyloid and tau buildup.
Read the full study here
Turmeric Root | STUDY 2
Turmeric Root | STUDY 2
Investigation of the effects of solid lipid curcumin on cognition and mood in a healthy older population – Cox et al. (2014)
Findings:
A 400 mg dose of solid lipid curcumin (Longvida®) improved attention, working memory, and mood in healthy adults, both acutely and over 4 weeks.
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers – Shoba et al. (1998)
Findings:
Piperine significantly enhances the absorption and bioavailability of curcumin in both animals and humans, overcoming curcumin’s naturally poor uptake.
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by combining it with piperine – Johnson et al. (2011)
Findings: Co-administering piperine with resveratrol significantly increased resveratrol’s bioavailability and peak serum concentration.
Read the full study
ALERTNESS / MOOD / MEMORY
Essential Focus & Energy
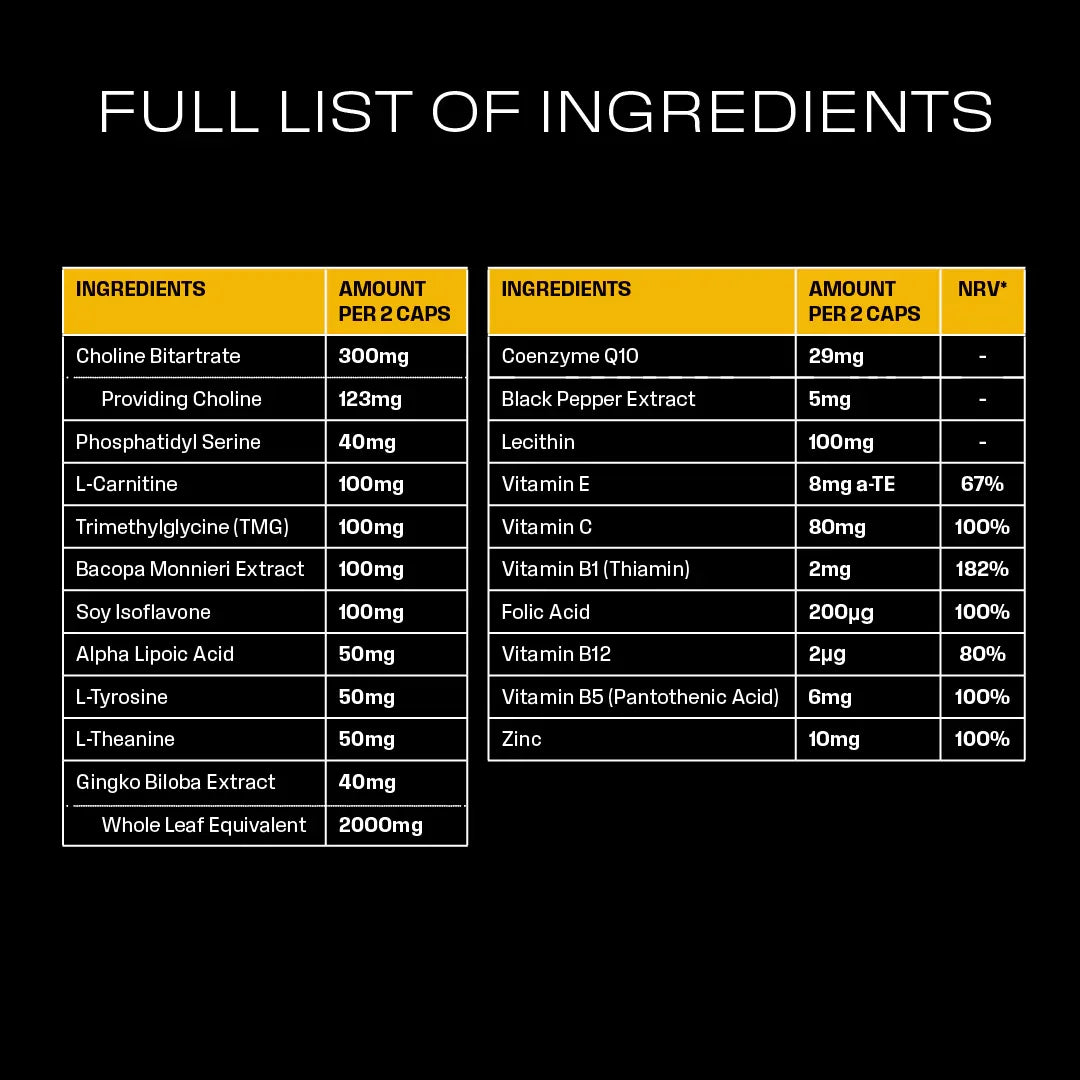
Choline Bitrate | STUDY 1
Choline Bitrate | STUDY 1
Dietary Choline Intake Is Beneficial for Cognitive Function and Delays Cognitive Decline: A 22-Year Large-Scale Prospective Cohort Study from China Health and Nutrition Survey – Huang et al. (2024)
Findings: Higher long-term dietary choline intake was associated with better cognitive performance and a slower rate of cognitive decline in Chinese adults aged 55–79.
Read the full study here
Choline Bitrate | STUDY 2
Choline Bitrate | STUDY 2
The relation of dietary choline to cognitive performance and white-matter hyperintensity in the Framingham Offspring Cohort – Poly et al. (2011)
Findings: Higher choline intake was associated with better memory performance and lower white matter damage in a large cohort of middle-aged and older adults
Read the full study
Phosphatidylserine | STUDY 1
Phosphatidylserine | STUDY 1
Effects of phosphatidylserine in age-associated memory impairment – Crook et al. (1991)
Findings:
Phosphatidylserine supplementation (100 mg three times daily for 12 weeks) improved memory performance in older adults with age-associated memory impairment.
Read the full study here
Phosphatidylserine | STUDY 2
Phosphatidylserine | STUDY 2
Soybean-derived phosphatidylserine improves memory function of the elderly Japanese subjects with memory complaints – Kato-Kataoka et al. (2010)
Findings:
Six months of soybean-derived phosphatidylserine (Soy-PS) improved memory in older adults with low baseline cognitive scores, particularly delayed verbal recall.
Read the full study
Acetyl-L-Carnitine | STUDY 1
Acetyl-L-Carnitine | STUDY 1
Long-term acetyl-L-carnitine treatment in Alzheimer's disease – Spagnoli et al. (1991)
Findings:
One year of acetyl-L-carnitine treatment slowed cognitive and functional decline in Alzheimer's patients compared to placebo.
Read the full study here
Acetyl-L-Carnitine | STUDY 2
Acetyl-L-Carnitine | STUDY 2
Meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled clinical trials of acetyl-L-carnitine vs. placebo in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease – Montgomery et al. (2003)
Findings: Acetyl-L-carnitine significantly improved cognitive function in individuals with MCI or mild Alzheimer’s disease across multiple trials.
Read the full study
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 1
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 1
Betaine supplementation lowers plasma homocysteine in healthy men and women – Steenge et al. (2003)
Findings: Betaine significantly reduced fasting and post-methionine load plasma homocysteine levels in adults with mildly elevated baseline levels
Read the full study here
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 2
Trimethylglycine | STUDY 2
Effects of betaine supplementation on cardiovascular markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis – Ashtary-Larky et al. (2021)
Findings: Low-dose betaine supplementation (<4 g/day) effectively lowers homocysteine without negatively impacting lipid profiles.
Read the full study
Bacopa Monnieri | STUDY 1
Bacopa Monnieri | STUDY 1
An acute, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study of 320 mg and 640 mg doses of Bacopa monnieri on sustained cognitive performance – Downey et al. (2013)
Findings:
A single 320 mg dose of Bacopa monnieri (CDRI 08) improved cognitive performance under mental fatigue in healthy adults.
Read the full study here
Bacopa Monnieri | STUDY 2
Bacopa Monnieri | STUDY 2
Efficacy of Standardized Extract of Bacopa monnieri (Bacognize®) on Cognitive Functions of Medical Students: A Six-Week, Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial – Kumar et al. (2016)
Findings:
Six weeks of Bacopa monnieri supplementation significantly improved cognitive functions in medical students.
Read the full study
Isoflavones | STUDY 1
Isoflavones | STUDY 1
Isoflavones and cognitive function in older women – Kritz-Silverstein et al. (2003)
Findings: Six months of soy isoflavone supplementation improved verbal memory and category fluency in postmenopausal women.
Read the full study here
Isoflavones | STUDY 2
Isoflavones | STUDY 2
Do soy isoflavones improve cognitive function in postmenopausal women? A meta-analysis – Cheng et al. (2014)
Findings:
Soy isoflavone supplementation shows modest but significant cognitive benefits in postmenopausal women, particularly for visual memory.
Read the full study
Alpha-Lipoic Acid | STUDY 1
Alpha-Lipoic Acid | STUDY 1
Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer's disease – Hager et al. (2007)
Findings:
Alpha-lipoic acid may help stabilize cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease over long-term use.
Read the full study here
Alpha-Lipoic Acid | STUDY 2
Alpha-Lipoic Acid | STUDY 2
A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial of omega-3 fatty acids and alpha-lipoic acid in Alzheimer's disease – Shinto et al. (2014)
Findings:
A combination of omega-3 fatty acids and alpha-lipoic acid may slow cognitive and functional decline in Alzheimer's patients.
Read the full study
Tyrosine | STUDY 1
Tyrosine | STUDY 1
Tyrosine improves cognitive performance and reduces blood pressure in cadets after one week of a combat training course – Deijen et al. (1999)
Findings:
Tyrosine supplementation improved memory and tracking performance and reduced systolic blood pressure in stressed military cadets.
Read the full study here
Tyrosine | STUDY 2
Tyrosine | STUDY 2
Tyrosine for Mitigating Stress and Enhancing Performance in Healthy Adult Humans: A Rapid Evidence Assessment – Attipoe et al. (2015)
Findings:
A review found consistent evidence that tyrosine improves cognitive performance under stress, but evidence for physical performance is inconclusive.
Read the full study
L-Theanine | STUDY 1
L-Theanine | STUDY 1
L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state - Nobre et al 2008
Findings: A 50mg dose of L-theanine significantly increased alpha brain wave activity, promoting relaxed alertness without drowsiness (p < 0.05).
L-Theanine| STUDY 2
L-Theanine| STUDY 2
The combination of L‑theanine and caffeine improves cognitive performance and increases subjective alertness – Giesbrecht et al. (2010)
Findings: A 97mg L-theanine + 40mg caffeine blend significantly improved task-switching accuracy and alertness while reducing tiredness in young adults
Read the full study
Ginkgo Biloba | STUDY 1
Ginkgo Biloba | STUDY 1
Neuropsychological changes after 30-day Ginkgo biloba administration in healthy participants – Stough et al. (2001)
Findings:
A 30-day trial found Ginkgo biloba significantly improved working memory, information processing speed, and executive function in healthy adults.
Read the full study here
Ginkgo Biloba | STUDY 2
Ginkgo Biloba | STUDY 2
The effects of acute doses of standardized Ginkgo biloba extract on memory and psychomotor performance in volunteers – Rigney et al. (1999)
Findings:
Acute doses of Ginkgo biloba extract improved working memory and psychomotor performance, particularly in participants aged 50–59.
Read the full study
CoQ10 | STUDY 1
CoQ10 | STUDY 1
Coenzyme Q10 Levels Associated With Cognitive Functioning and Executive Function in Older Adults – Fernández-Portero et al. (2022)
Findings:
Higher plasma CoQ10 levels are significantly associated with better cognitive and executive functioning in older adults.
Read the full study here
CoQ10 | STUDY 2
CoQ10 | STUDY 2
Coenzyme Q10 administration increases brain mitochondrial concentrations and exerts neuroprotective effects – Matthews et al. (1998)
Findings: Oral CoQ10 increases brain and mitochondrial levels and shows neuroprotective effects in models of neurodegeneration
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers – Shoba et al. (1998)
Findings:
Piperine significantly enhances the absorption and bioavailability of curcumin in both animals and humans, overcoming curcumin’s naturally poor uptake.
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by combining it with piperine – Johnson et al. (2011)
Findings: Co-administering piperine with resveratrol significantly increased resveratrol’s bioavailability and peak serum concentration.
Read the full study
Lecithin | STUDY 1
Lecithin | STUDY 1
Natural lecithin promotes neural network complexity and activity – Latifi et al. (2016)
Findings:
Natural lecithin rich in brain-like polyunsaturated fatty acids enhances neuronal growth, synaptic activity, and network complexity in vitro.
Read the full study here
Vitamin E | STUDY 1
Vitamin E | STUDY 1
Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM-AD VA cooperative randomized trial – Dysken et al. (2014)
Findings:
High-dose vitamin E slowed functional decline in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease compared to placebo.
Read the full study here
Vitamin E | STUDY 2
Vitamin E | STUDY 2
Vitamin E and cognitive decline in older persons – Morris et al. (2002)
Findings:
Higher vitamin E intake is linked to slower cognitive decline in older adults over time.
Read the full study
Vitamin C | STUDY 1
Vitamin C | STUDY 1
Plasma Vitamin C Concentrations and Cognitive Function: A Cross-Sectional Study – Travica et al. (2019)
Findings:
Adequate plasma vitamin C levels are associated with better performance on memory, attention, and decision-making tasks.
Read the full study here
Vitamin C | STUDY 2
Vitamin C | STUDY 2
Vitamin C Status and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review – Travica et al. (2017)
Findings:
Higher vitamin C levels are associated with better cognitive performance in healthy individuals, highlighting the nutrient’s neuroprotective potential.
Read the full study
Thiamine | STUDY 1
Thiamine | STUDY 1
Supplemental thiamine as a practical, potential way to prevent Alzheimer's disease from commencing – Fessel (2021)
Findings:
Thiamine supplementation may help prevent Alzheimer's disease if given early, before cognitive symptoms begin.
Read the full study here
Thiamine | STUDY 2
Thiamine | STUDY 2
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) and dementia – Gibson et al. (2016)
Findings:
Thiamine deficiency impairs brain glucose metabolism and mimics Alzheimer's-like symptoms, highlighting its potential role in dementia prevention.
Read the full study
Folate | STUDY 1
Folate | STUDY 1
Effect of 3-year folic acid supplementation on cognitive function in older adults in the FACIT trial: a randomised, double blind, controlled trial – Durga et al. (2007)
Findings:
Three years of folic acid supplementation improved memory and information processing in older adults with elevated homocysteine.
Read the full study here
Folate | STUDY 2
Folate | STUDY 2
Effects of folic acid supplementation on cognitive function and inflammation in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment – Wang et al. (2024)
Findings:
Folic acid supplementation improved cognitive performance and reduced inflammatory markers in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Read the full study
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows the rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial – Smith et al. (2010)
Findings: Low vitamin B-12 status and elevated homocysteine or MMA levels significantly accelerated cognitive decline, while folate showed no effect.
Read the full study her
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 and cognitive function in older persons – Doets et al. 2012
Findings: Low levels of sensitive markers like MMA and holotranscobalamin were associated with cognitive decline.
Read the full study
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 1
Cerebral deficiency of vitamin B5 as a potentially-reversible cause of neurodegeneration and dementia in sporadic Alzheimer's disease – Xu et al. (2020)
Findings:
Severe cerebral vitamin B5 deficiency was found in Alzheimer’s disease brains, particularly in regions most affected by neurodegeneration.
Read the full study here
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 2
Substantively Lowered Levels of Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) in Several Regions of the Human Brain in Parkinson’s Disease Dementia – Scholefield et al. (2021)
Findings:
Vitamin B5 levels are significantly reduced in key brain regions of individuals with Parkinson’s disease dementia, mirroring patterns seen in Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease.
Read the full study
Zinc | STUDY 1
Zinc | STUDY 1
Zinc and human health: an update – Chasapis et al. (2012)
Findings: Zinc plays a crucial role in immune function, oxidative stress regulation, and chronic disease prevention, with deficiency linked to a wide range of health issues
Read the full study here
Zinc | STUDY 1
Zinc | STUDY 1
Effects of zinc supplementation on cognitive function in healthy middle-aged and older adults: the ZENITH study – Maylor et al. (2006)
Findings: Zinc supplementation showed modest short-term cognitive benefits in healthy older adults, particularly in spatial working memory.
Read the full study here
FOCUS / CLARITY / MEMORY
Essential Lions Mane Extract
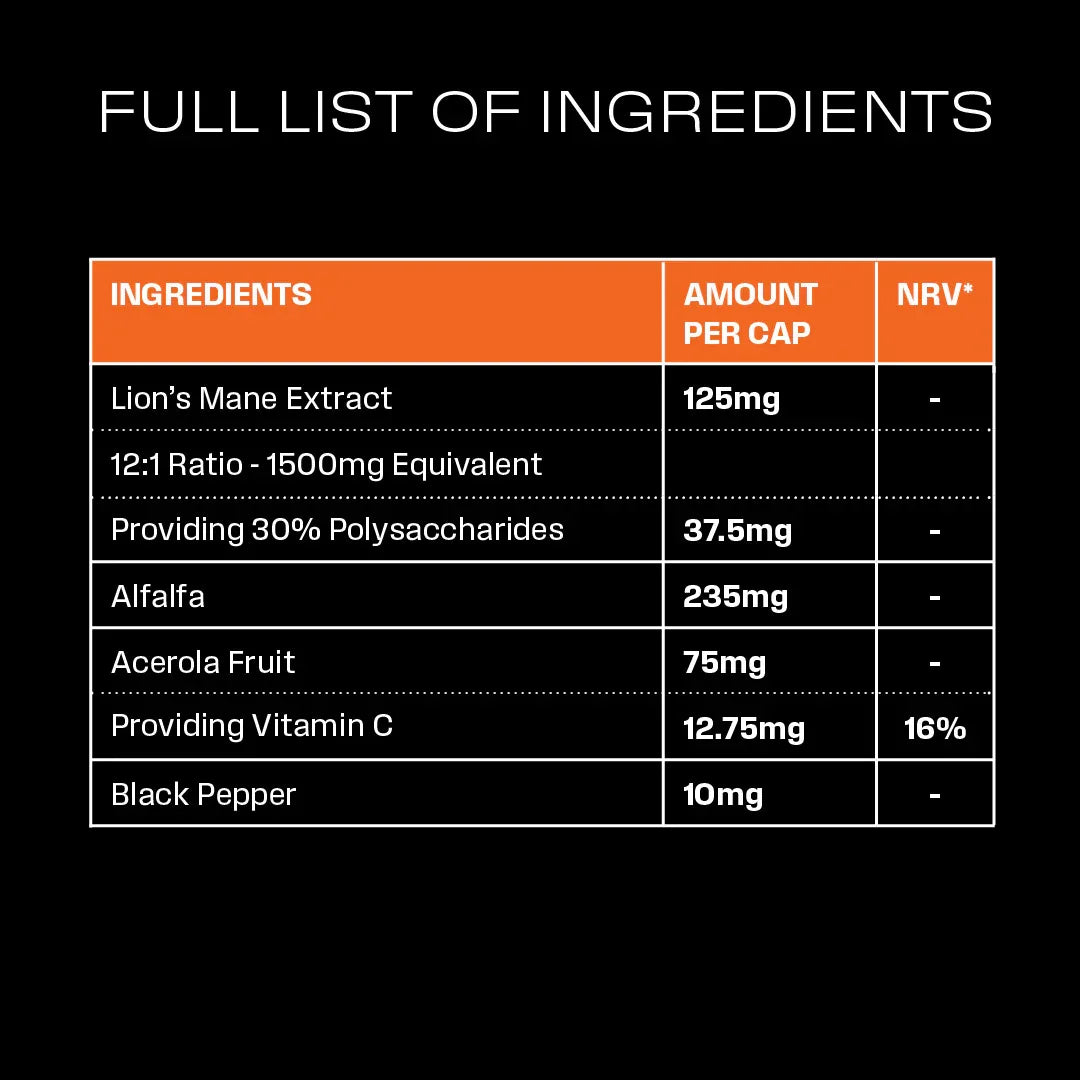
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Lions Mane | STUDY 1
Improving effects of the mushroom Hericium erinaceus on mild cognitive impairment: a double‑blind placebo‑controlled clinical trial – Mori et al. (2009)
Findings: Hericium erinaceus (Yamabushitake) significantly improved cognitive function in adults with mild cognitive impairment over 16 weeks, with no adverse effects.
Read the full study here
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
Lions Mane | STUDY 2
The Acute and Chronic Effects of Lion's Mane Mushroom Supplementation on Cognitive Function, Stress and Mood in Young Adults - Doucherty et al (2023)
Findings: A single 1.8g dose of Hericium erinaceus significantly improved cognitive speed in healthy young adults, with signs of reduced stress after 28 days.
Read the full study
Alfalfa | STUDY 1
Alfalfa | STUDY 1
The effects of alfalfa powder combined with health education on patients with dyslipidemia: A randomized controlled trial – Pei Wang et al. (2024)
Findings: Alfalfa powder combined with health education significantly lowered total cholesterol, LDL-C, and Apo A1 in dyslipidemia patients, likely through changes in glycerophospholipid metabolism.
Read the full study here
Acerola | STUDY 1
Acerola | STUDY 1
Acerola, an untapped functional superfruit: a review on latest frontiers – Prakash & Baskaran (2018)
Findings:
Acerola is one of the richest natural sources of vitamin C and contains potent phytonutrients with antioxidant, anti-aging, and functional food properties.
Read the full study here
Acerola | STUDY 2
Acerola | STUDY 2
Vitamin C Status and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review – Travica et al. (2017)
Findings: Higher vitamin C levels are associated with better cognitive performance in healthy individuals, highlighting the nutrient’s neuroprotective potential.
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Black Pepper | STUDY 1
Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers – Shoba et al. (1998)
Findings: Piperine significantly enhances the absorption and bioavailability of curcumin in both animals and humans, overcoming curcumin’s naturally poor uptake.
Read the full study
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Black Pepper | STUDY 2
Enhancing the bioavailability of resveratrol by combining it with piperine – Johnson et al. (2011)
Findings: Co-administering piperine with resveratrol significantly increased resveratrol’s bioavailability and peak serum concentration.
Read the full study
BALANCE / VITALITY / WELLNESS
Essential Multivitamin + Iron
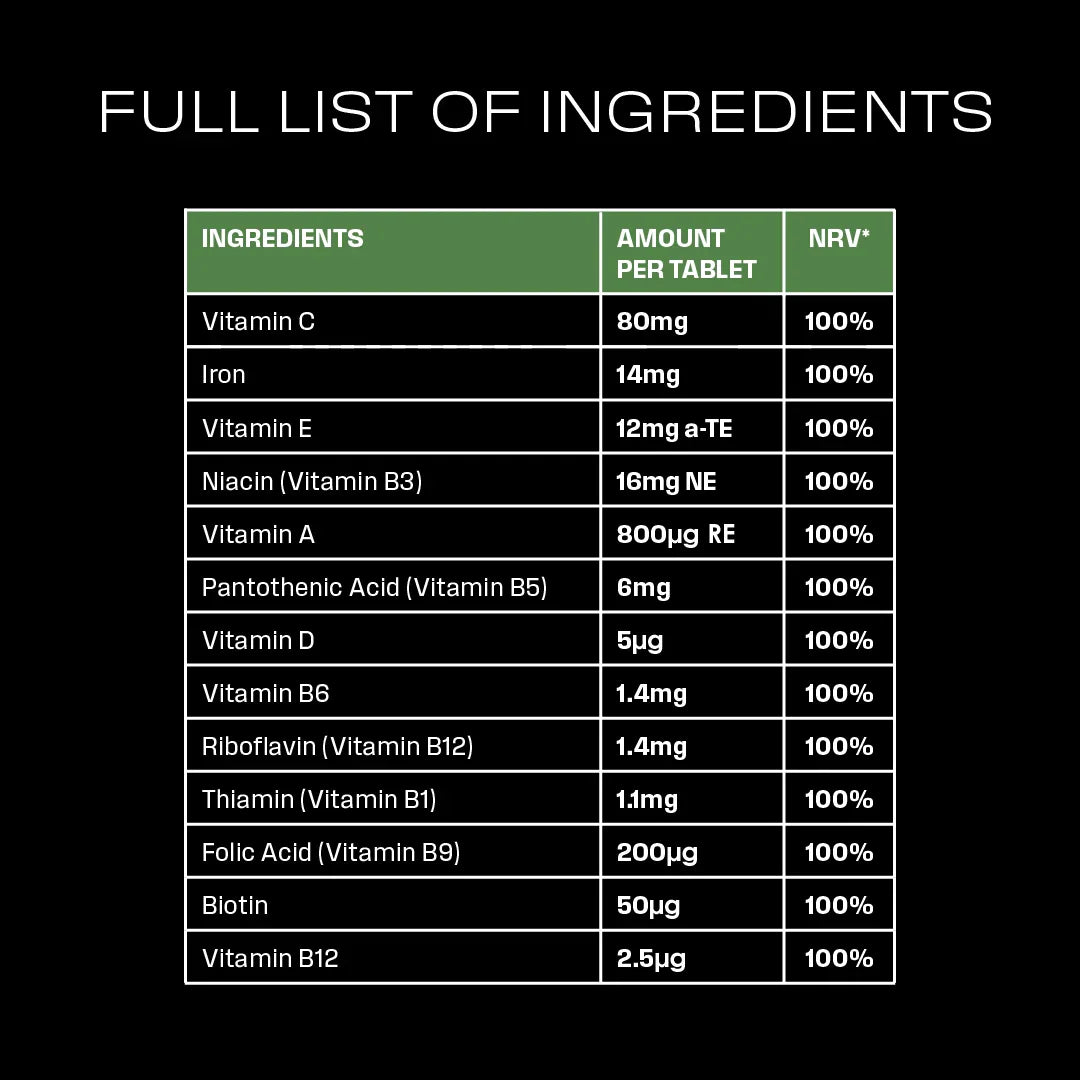
Vitamin C | STUDY 1
Vitamin C | STUDY 1
Plasma Vitamin C Concentrations and Cognitive Function: A Cross-Sectional Study – Travica et al. (2019)
Findings: Adequate plasma vitamin C levels are associated with better performance on memory, attention, and decision-making tasks.
Vitamin C | STUDY 2
Vitamin C | STUDY 2
Vitamin C Status and Cognitive Function: A Systematic Review – Travica et al. (2017)
Findings: Higher vitamin C levels are associated with better cognitive performance in healthy individuals, highlighting the nutrient’s neuroprotective potential.
Read the full study
Iron | STUDY 1
Iron | STUDY 1
The effects of oral iron supplementation on cognition in older children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis – Falkingham et al. (2010)
Findings:
Iron supplementation improved attention, concentration, and IQ in anaemic individuals.
Iron | STUDY 2
Iron | STUDY 2
Impact of Iron Intake and Reserves on Cognitive Function in Young University Students – Dimas-Benedicto et al. (2024)
Findings:
Iron intake and serum ferritin levels are positively associated with cognitive performance in university students.
Vitamin E | STUDY 1
Vitamin E | STUDY 1
Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM-AD VA cooperative randomized trial – Dysken et al. (2014)
Findings:
High-dose vitamin E slowed functional decline in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease compared to placebo.
Vitamin E | STUDY 2
Vitamin E | STUDY 2
Vitamin E and cognitive decline in older persons – Morris et al. (2002)
Findings:
Higher vitamin E intake is linked to slower cognitive decline in older adults over time.
Niacin | STUDY 1
Niacin | STUDY 1
The association of sleep quality and insomnia with dietary intake of tryptophan and niacin – Verster et al. (2015)
Findings:
Higher dietary intake of tryptophan and niacin was modestly but significantly associated with lower insomnia scores and improved sleep quality, especially in men.
Niacin | STUDY 2
Niacin | STUDY 2
Nicotinic acid promotes sleep through prostaglandin synthesis in mice – Szentirmai & Kapás (2019)
Findings:
Nicotinic acid significantly increased non-REM sleep in mice via prostaglandin-mediated activation of the GPR109A receptor, independent of body temperature changes.
Vitamin A | STUDY 1
Vitamin A | STUDY 1
Structural, functional, nutritional and clinical aspects of vitamin A: A review – Menezes & Almeida (2024)
Findings:
Vitamin A is essential for vision, immunity, cell growth, and reproduction, with clinical applications and risks tied to both deficiency and excess.
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 1
Cerebral deficiency of vitamin B5 (d-pantothenic acid; pantothenate) as a potentially-reversible cause of neurodegeneration and dementia in sporadic Alzheimer's disease – Xu et al. (2020)
Findings:
Severe cerebral vitamin B5 deficiency was found in Alzheimer’s disease brains, particularly in regions most affected by neurodegeneration.
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B5 | STUDY 2
Substantively Lowered Levels of Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) in Several Regions of the Human Brain in Parkinson’s Disease Dementia – Scholefield et al. (2021)
Findings:
Vitamin B5 levels are significantly reduced in key brain regions of individuals with Parkinson’s disease dementia, mirroring patterns seen in Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease.
Vitamin D | STUDY 1
Vitamin D | STUDY 1
Meta-analysis of memory and executive dysfunctions in relation to vitamin D – Annweiler et al. (2013)
Findings:
Lower vitamin D levels are significantly associated with executive dysfunction, particularly in mental shifting and processing speed, but show only modest links to episodic memory.
Vitamin D | STUDY 2
Vitamin D | STUDY 2
Vitamin D and cognition in older adults: updated international recommendations – Annweiler et al. (2014)
Findings:
International experts agree that vitamin D deficiency increases dementia risk in older adults and warrants screening, though it is not yet a diagnostic tool for cognitive decline.
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
A combination of melatonin, vitamin B6 and medicinal plants in the treatment of mild-to-moderate insomnia: A prospective pilot study – Lemoine et al. (2019)
Findings:
A 2-week combination of melatonin, vitamin B6, and plant extracts significantly improved sleep quality, onset, and duration in individuals with mild-to-moderate insomnia.
Vitamin B Complex | STUDY 2
Vitamin B Complex | STUDY 2
B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review – Kennedy (2016)
Findings:
All eight B vitamins are essential for brain health, yet most studies and supplements focus too narrowly on B6, B9, and B12.
Vitamin B2 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B2 | STUDY 1
Effectiveness of high-dose riboflavin in migraine prophylaxis: A randomized controlled trial – Schoenen et al. (1998)
Findings:
High-dose riboflavin (400 mg/day) significantly reduces migraine attack frequency and headache days with minimal side effects.
Vitamin B2 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B2 | STUDY 2
Riboflavin Has Neuroprotective Potential: Focus on Parkinson’s Disease and Migraine – Marashly & Bohlega (2017)
Findings:
Riboflavin may protect against neurological disorders by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Vitamin B1 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B1 | STUDY 1
Supplemental thiamine as a practical, potential way to prevent Alzheimer's disease from commencing – Fessel (2021)
Findings:
Thiamine supplementation may help prevent Alzheimer's disease if given early, before cognitive symptoms begin.
Vitamin B1 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B1 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) and dementia – Gibson et al. (2016)
Findings:
Thiamine deficiency impairs brain glucose metabolism and mimics Alzheimer's-like symptoms, highlighting its potential role in dementia prevention.
Vitamin B9 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B9 | STUDY 1
Effect of 3-year folic acid supplementation on cognitive function in older adults in the FACIT trial: a randomised, double blind, controlled trial – Durga et al. (2007)
Findings:
Three years of folic acid supplementation improved memory and information processing in older adults with elevated homocysteine.
Vitamin B9 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B9 | STUDY 2
Effects of folic acid supplementation on cognitive function and inflammation in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials – Wang et al. (2024)
Findings:
Folic acid supplementation improved cognitive performance and reduced inflammatory markers in older adults with mild cognitive impairment.
Vitamin B7 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B7 | STUDY 1
Effects of biotin deficiency on short term memory: The role of glutamate, glutamic acid, dopamine and protein kinase A – Munzuroğlu et al. (2022)
Findings:
Biotin deficiency impairs short-term memory and locomotor activity by lowering dopamine levels and protein kinase A (PKA) activity in the hippocampus.
Vitamin B7 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B7 | STUDY 2
Biotin: biochemical, physiological and clinical aspects – Said (2011)
Findings:
Biotin is essential for human growth and development, and its deficiency can lead to serious neurological, dermatological, and developmental disorders.
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 1
Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows the rate of brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial – Smith et al. (2010)
Findings:
Low vitamin B-12 status and elevated homocysteine or MMA levels significantly accelerated cognitive decline, while folate showed no effect.
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B12 and cognitive function in older persons – Doets et al. 2012
Findings:
Vitamin B12 intake alone showed no consistent link to cognitive function, but low levels of sensitive markers like MMA and holotranscobalamin were associated with cognitive decline.
CALM / RELAXATION / RECOVERY
Essential Magnesium Complex
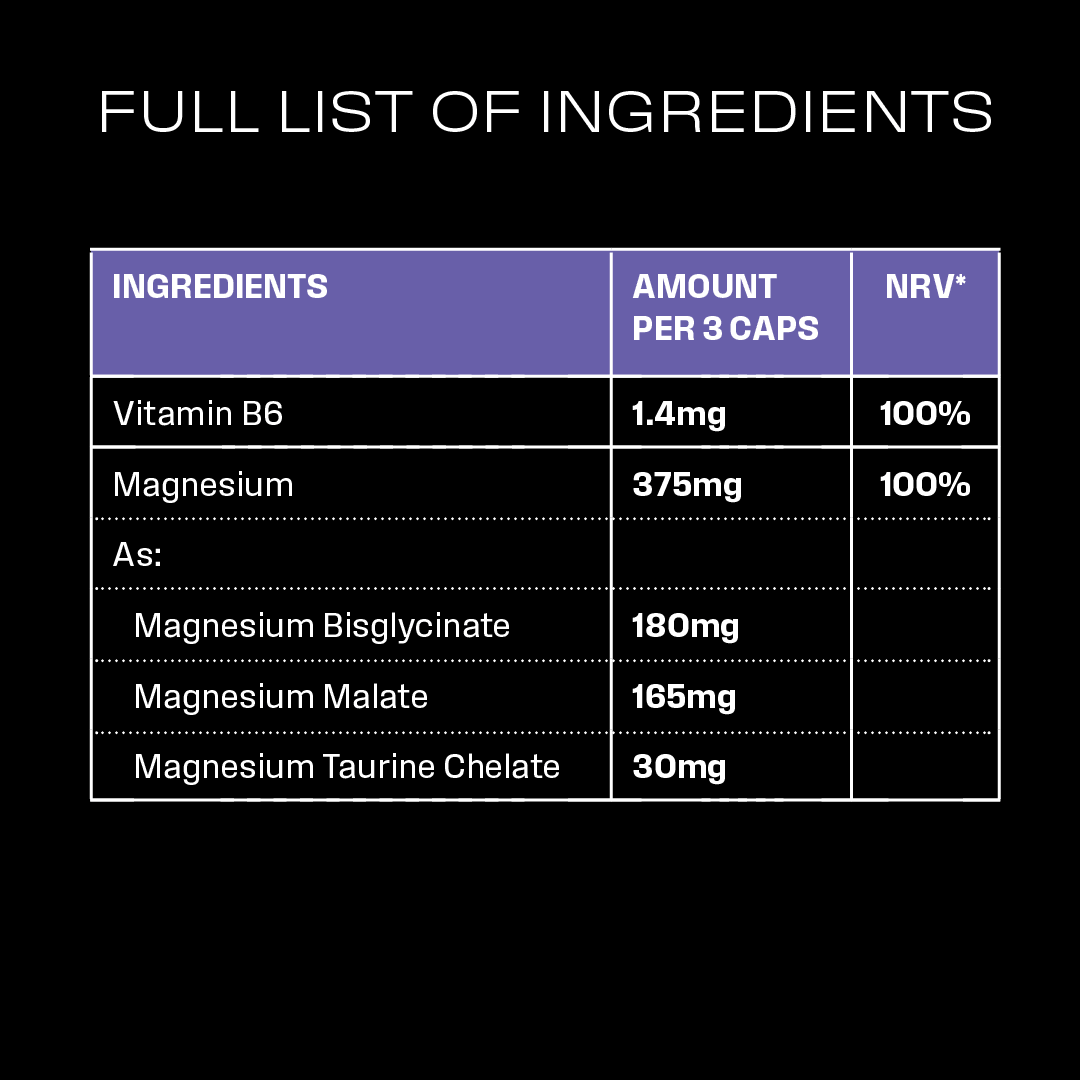
Magnesium | STUDY 1
Magnesium | STUDY 1
The Role of Magnesium Therapy in Learning and Memory – Hoane (2010)
Findings: Magnesium influences learning and memory in both healthy and injured brains, showing dose- and task-dependent effects on cognitive function and recovery.
Read the full study here
Magnesium | STUDY 2
Magnesium | STUDY 2
Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions – Al Alawi et al. (2018)
Findings: Magnesium is critical to human health, with deficiency linked to a wide range of chronic, neurological, cardiovascular, and metabolic diseases.
Read the full study
Magnesium | STUDY 3
Magnesium | STUDY 3
Examining the Effects of Supplemental Magnesium on Self-Reported Anxiety and Sleep Quality: A Systematic Review (Rawji et al 2024)
Findings: This systematic review found that magnesium supplementation may improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety, particularly at higher doses and when combined with vitamin B6
Read the full study here
Magnesium | STUDY 4
Magnesium | STUDY 4
Magnesium and the Brain: A Focus on Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration – Maier et al. (2023)
Findings: Magnesium plays a critical neuroprotective role by modulating inflammation, maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity, and regulating processes linked to neurodegeneration.
Read the full study
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 1
A combination of melatonin, vitamin B6 and medicinal plants in the treatment of mild-to-moderate insomnia: A prospective pilot study – Lemoine et al. (2019)
Findings: A 2-week combination of melatonin, vitamin B6, and plant extracts significantly improved sleep quality, onset, and duration in individuals with mild-to-moderate insomnia.
Read the full study here
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 2
Vitamin B6 | STUDY 2
B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review – Kennedy (2016)
Findings: All eight B vitamins are essential for brain health, yet most studies and supplements focus too narrowly on B6, B9, and B12.
Read the full study
HEART / BRAIN / VITALITY44
Essential Omega 3
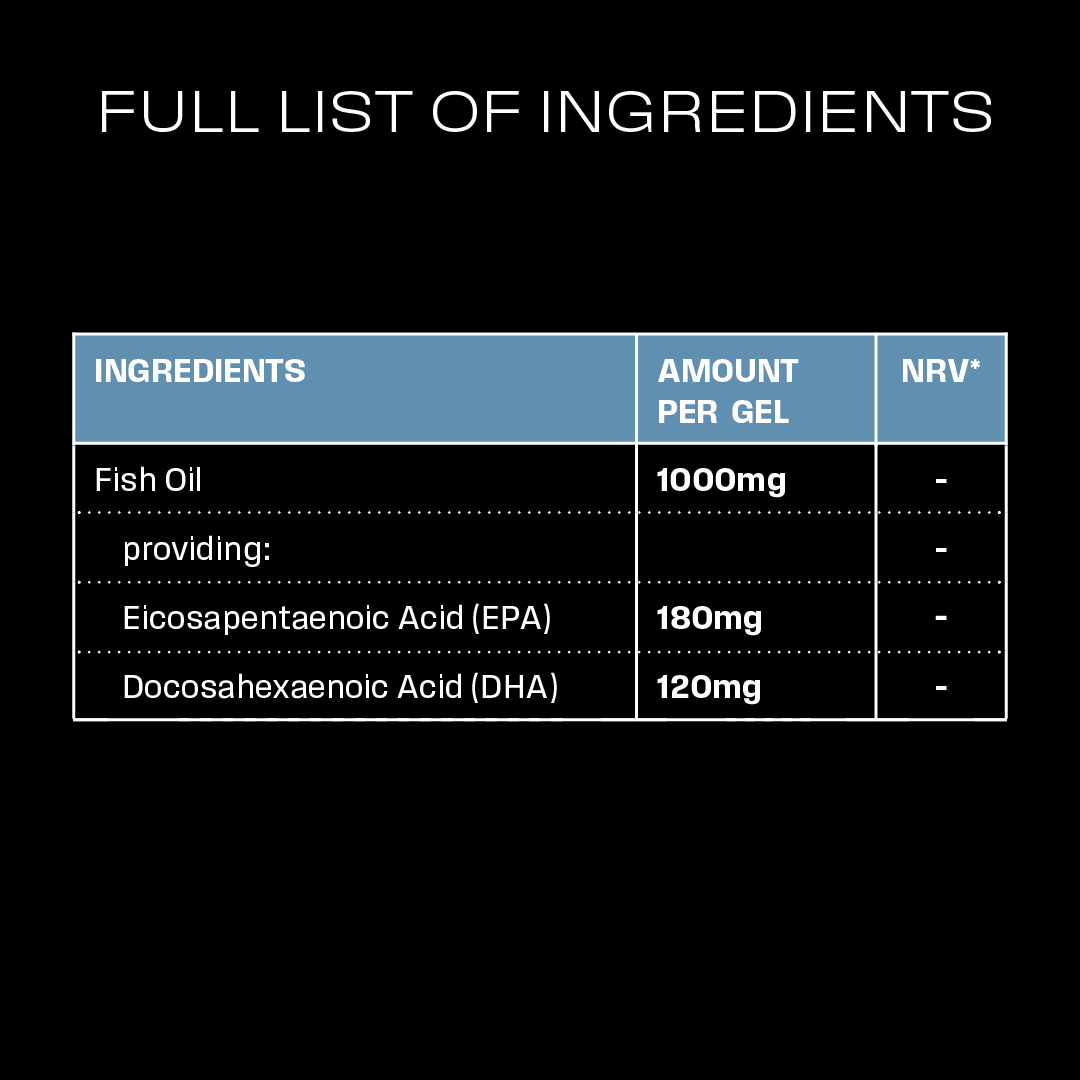
DHA | STUDY 1
DHA | STUDY 1
Beneficial effects of docosahexaenoic acid on cognition in age-related cognitive decline – Yurko-Mauro et al. (2010)
Findings: DHA supplementation improved memory and learning in older adults with age-related cognitive decline.
EPA and DHA | STUDY 1
EPA and DHA | STUDY 1
Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: health benefits throughout life – Swanson et al. (2012)
Findings: EPA and DHA are essential omega-3 fatty acids with benefits for cognitive function, especially in early Alzheimer’s disease.
Read the full study

